🗽 Early Republic
November 9, 2022
Themes
- Philosophical differences between the Federalists and the Anti-federalists
- Hamilton vs Jefferson dynamic
- Economic differences (agrarian vs industrial)
- North vs South (sectionalism)
- Foreign policy
- England/Europe vs Napoleon
Washington’s Government
- Establishes a dignified office that was independent
- Worried about federal power vs insuring individual liberty
- First cabinet shows balance
- Secretary of Treasury - Hamilton
- Secretary of State - Jefferson
Events
- Whiskey Rebellion (1794)
- Byproduct of Hamilton’s tax plan
- Foil to Shay’s rebellion
- Proclamation of Neutrality (1793)
- Washington makes a proclamation that the United States will stay neutral in the war between England and France
- Citizen Genêt Affair (1793)
- Charles Genêt wanted to promote war against England & Spain
- Washington let Genêt stay in the US instead of stopping him; shows grace
Judging John Adams
Election of 1796
- Bitter party politics
- Feds led by Hamilton plant own destruction
- Hamilton divides the Feds
- Allows Jefferson to win the vice presidency
- Executive Branch split Fed/Republic
XYZ Affair
- The Jay Treaty - pro England
- Quasi naval way with France
- US representatives humiliated by French government
- Feds want war, but Adams resists
1798 - Alien + Sedition Acts
- No war, but let’s appease Hamilton
- Limited free speech, reduced allowed immigration, limited free press
- Attacks 1st amendment
- Aimed at Jeffersonians squarely (bad)
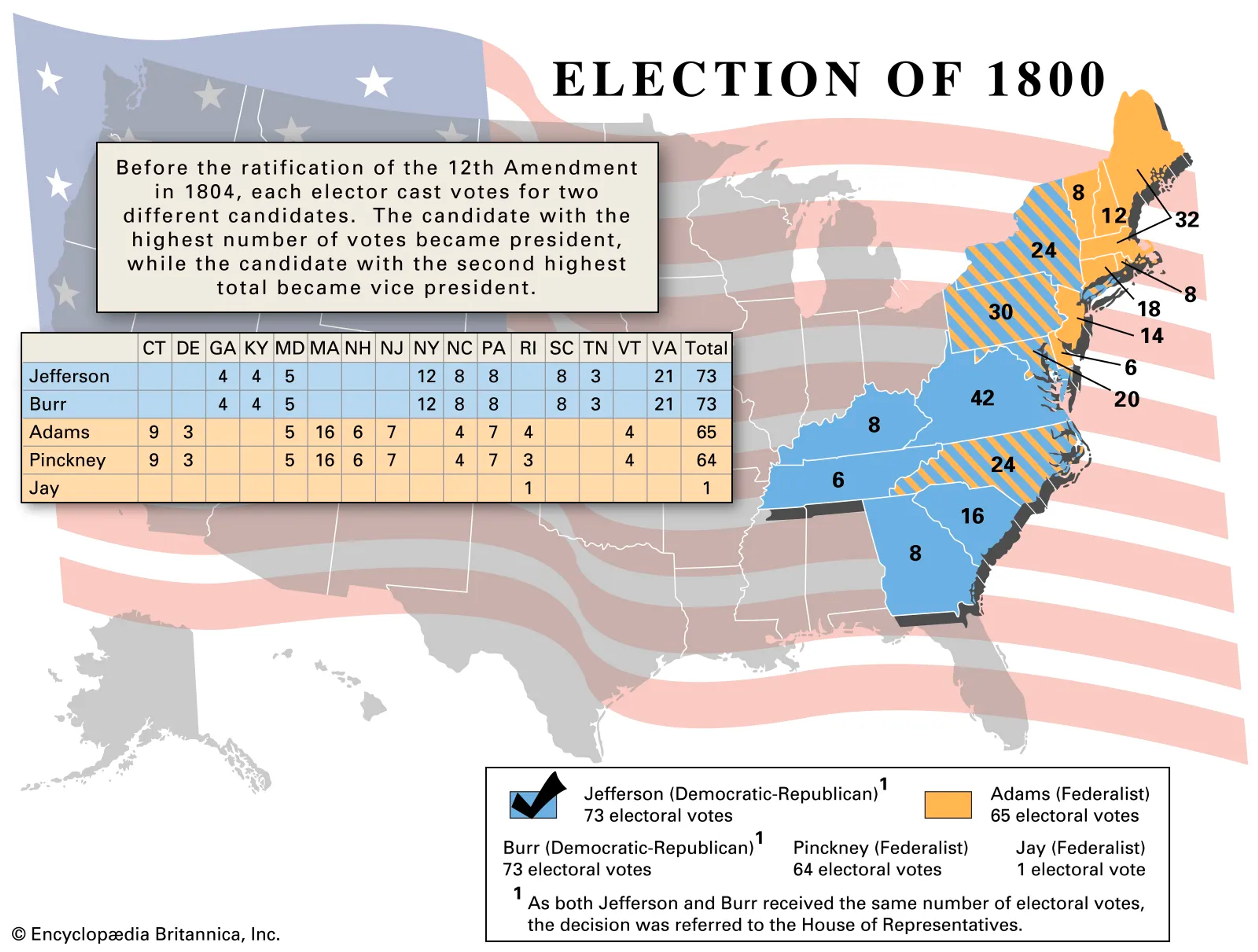
Election of 1800
- Adams bid for a-election vs. Jefferson + Burr.
- Feds. still divided, Hamilton wants to punish Adams.
- Also, save America from Jeffersonianism
- Problem — Electoral college didn’t work
- Jefferson / Burr tied at 73
- Went to the house, 36 votes later, Hamilton breaks the tie for Jefferson
- Hamilton hated Jefferson, but he feared Burr.
Impacts
- Jeffersonian take-over of the Executive / Legislature branches
- Feds are dead
- 12th amendment added
- Burr kills Hamilton
Jeffersonian Ascent
Jeffersonian Society
- Self-confident, assertive, blatantly racist, no regard for social class.
- Sectionalism ↑
- Words “northerner” & “southerner” emerge
Jefferson as President
- Hugely informal
- Never veto’d a thing
Goals
- Repeal alien + Sedition
- Reduce the size and cost of the federal government
- Military size was cut in half
- International peace
1803 - Louisiana Purchase
- Louisiana Territory was acquired for $15 million from France; bypasses congress
- Establishes the United States as a continental empire
- Leads to future problems, too
Problems for Jefferson
- First term super successful, second term was lacking.
- 1801 - 1805 → Undeclared naval war with North African Barbary pirates
- “Quids” → Extremist Jeffersonians emerge (T.Sepp’s party divides)
- Yazoo land fraud
- 1804 → Aaron Burr shoots Hamilton
Ending the International Slave Trade
- Politically, no one’s happy
- Domestically, it increases chattel slavery. 😟
1807 - The Embargo Act
- Against England
- Predictably divides the nation
- Economic recession due to the embargo, especially hard in the North
⭐ 1805 - Marbury v. Madison
- Establishes judicial review (their greatest power)
I could beat Up Jefferson in a fight. Might have some creative combos tho, Diff: 6/10 -J
could you beat up Washington
No. no i could not. 10/10 diff -J
“Geography of reality and the geography of hope were clashing.” - Funny history lad
James Madison
- For Madison, being president was duty
- Political genius; lacked leadership traits
- Federalists resist, anti-embargo
War of 1812
- Madison oddly declared war
- Jeffersonianism leaves
- ⭐ Turning point; US political leadership changes
- Non-founding leaders (war hawks → Henry Clay & John C. Calhoun)
- Andrew Jackson becomes the star
James Monroe
- The last of the Virginia dynasty
- Secretary of state, military officer
- Not as sharp as Jefferson or Madison
1823 - Monroe Doctrine
- Nationalism applied to foreign policy
- Latin America gains independence; we tell Europe to stay away or else
- If Europe interfered, we would fight them.