👑 Pre-Europe/Colonial America
November 7, 2022
God & Gold 👑
- The Spanish’s main motive to explore and conquest America was god and gold.
- The queen of Spain wanted to expand Catholicism (God) to America.
- Spain also wanted money (gold) to expand its empire.
Three Sisters (Corn, Beans, Squash) 🌽
- Global trading was prominent before most major exports used today (Planes, Amazon, Cargo Crates, etc.)
- Fall of Constantinople + Spanish Reconquista → Age of exploration → Columbus contact → 500 year conflict between natives, Europeans, and African Americans.
- Matrilineal Lineage (female decent)
- Mississippi river was the major trading route.
Spanish Imperialism 🇪🇸
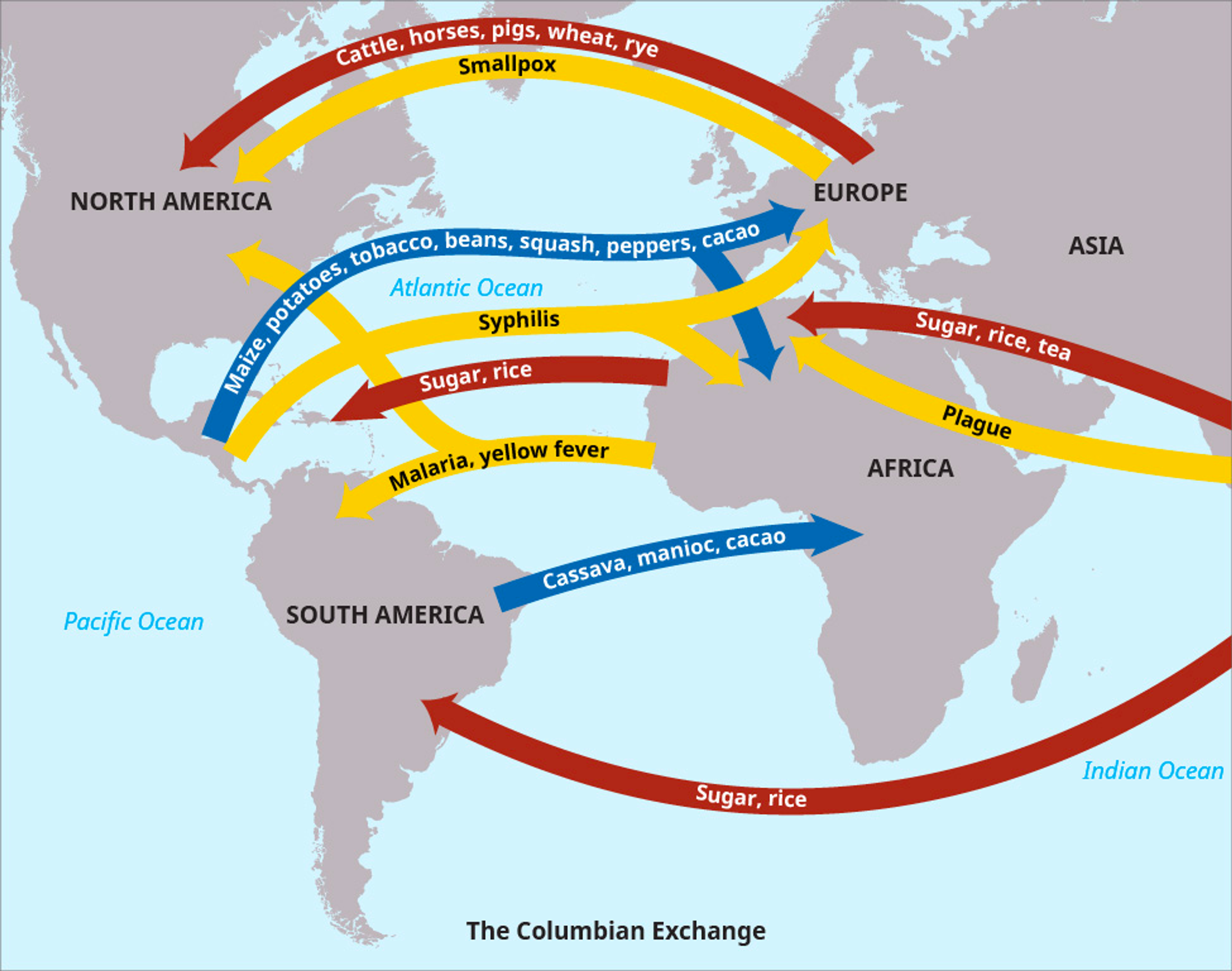
Columbian Exchange ⭐️
- Columbian trade system that emerges after European contact (early globalization)
- Europeans traded various items to/from the Americas (such as sugar, beans, cattle, etc.)
- This also transferred diseases between Europeans and Americans.
- Smallpox killed millions in the Americas because the Americans had no immune system to support the disease. (syphilis, yellow fever)
- This ultimately led to the slavery of Africans because the Europeans wanted people to farm the things they wanted (like tobacco).
- Evolved into “Triangular Trade” + “Mercantilism”
Encomienda System ⭐️
- The Spanish land, economic, and agricultural control system that emerged in the 1500s.
- Natives would work en masse, in return, they receive education + Christianization
- en masse: in a group; all together.
- There were/are accusations of systematic abuse/rape/murder
Oñate and Today
- This article is important to us today because people are destroying the statue of Oñate.
- People are mad that Oñate killed people in the Spanish encomienda system and he has a statue.
Reading 📖
Juan Gines de Sepulveda 🇪🇸
- This talks more about the historical significance of the Spanish conquering the Native Americans.
- It talks about the Spanish’s point of view of the Natives, such as the Aztecs, — ”with this ritual they believed that they had appeased their gods. They also ate the flesh of the sacrificed men…”
- Juan Gines de Sepulveda was more in favor of the Spanish, not the natives.
- He believed that the Native Americas had no ruler(s), no laws, and they were barbarian.
Bartolomé de las Casas 💢
- This is more about the actual destruction of the Native Americans, and how many of them died.
- “[the] Spaniards, who no sooner had knowledge of these people than they became like fierce wolves and tigers and lions who have gone many days without food or nourishment.”
- Bartolomé de las Casas was more in favor of the natives, pointing out the Spanish committed atrocities against the natives — such as killing the natives.
Colonization in America 🏝
English Colonization
- Religious outcasts
- Cash crop → making money in America
- Control either through settlers, corporations, or salutary neglect
French Colonization
- More about native alliance + trade
Jamestown
- Founded in 1607 in Virginia by the London Company.
- It was the first colony in America
- Jamestown earned a lot of its money from cash crops, specifically tobacco.
- Terrible land + disease → starving times
- Martial law
- John Smith (bad guy) 👹
Colonial Economics 💵
- Most of the colonies in the Americas were owned by companies
- These companies wanted money.
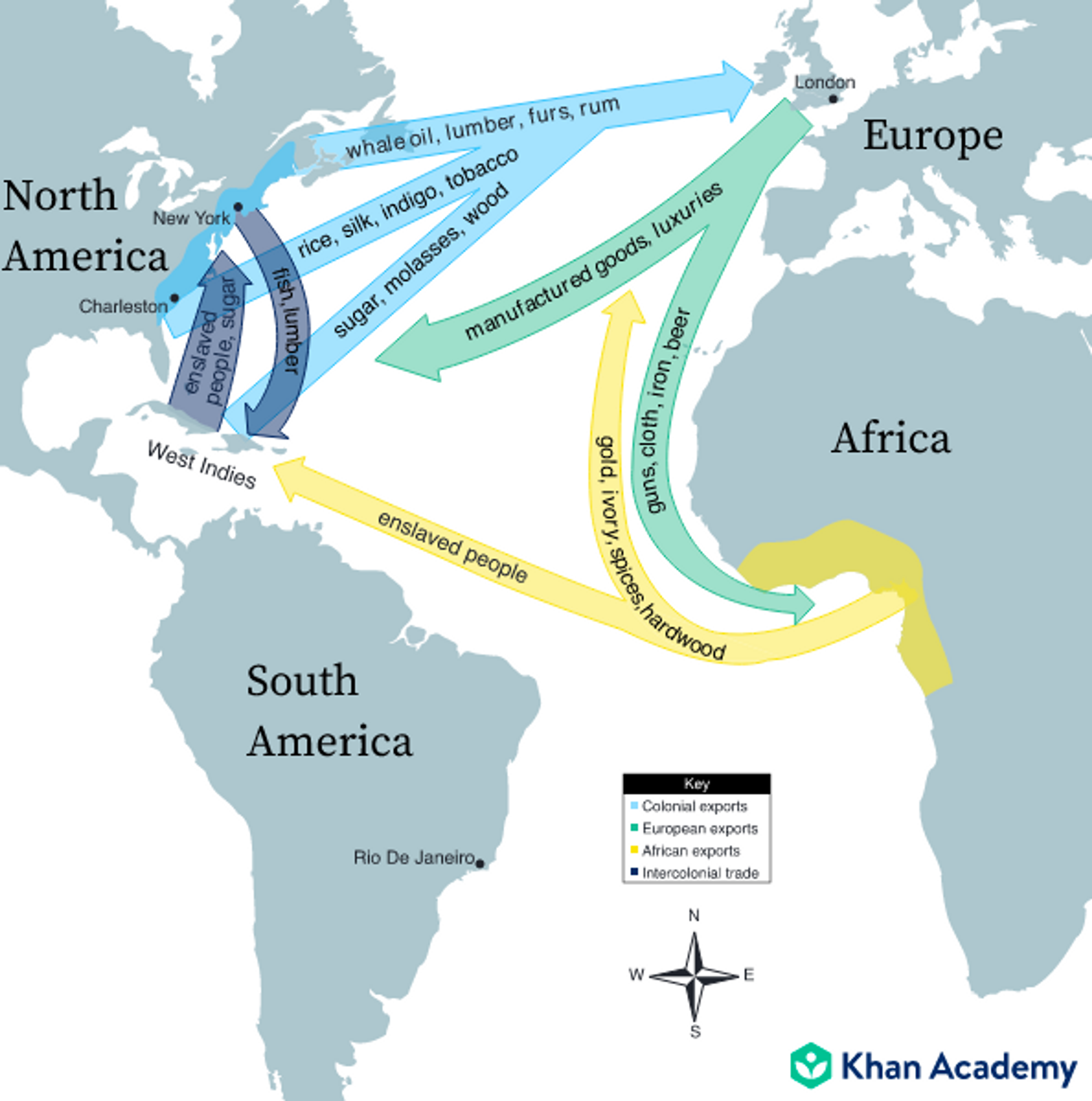
- This led to a mercantile economy
- Mercantilism → colonies send raw materials (such as cotton) to the mother country and the mother country sends processed materials back (such as textiles).
- Manifested by triangular trade.
- Similar to the Colombian exchange, but includes slaves.
- No ship could trade in the colonies unless it was either built in England, or the crew was English.
- This led to a monopoly of the colonies by England. (economic slavery)
Slavery Develops
- Native Americans and poor European indentured servants
- Indentured servant → Poor white European who would sell themselves to someone wealthy for a term of around 7 years with no pay, guarantees new world passage, food, and place to stay
- First African slaves were imported in 1619 to Virginia.
- Slavery originated from Muslims and other African tribes.
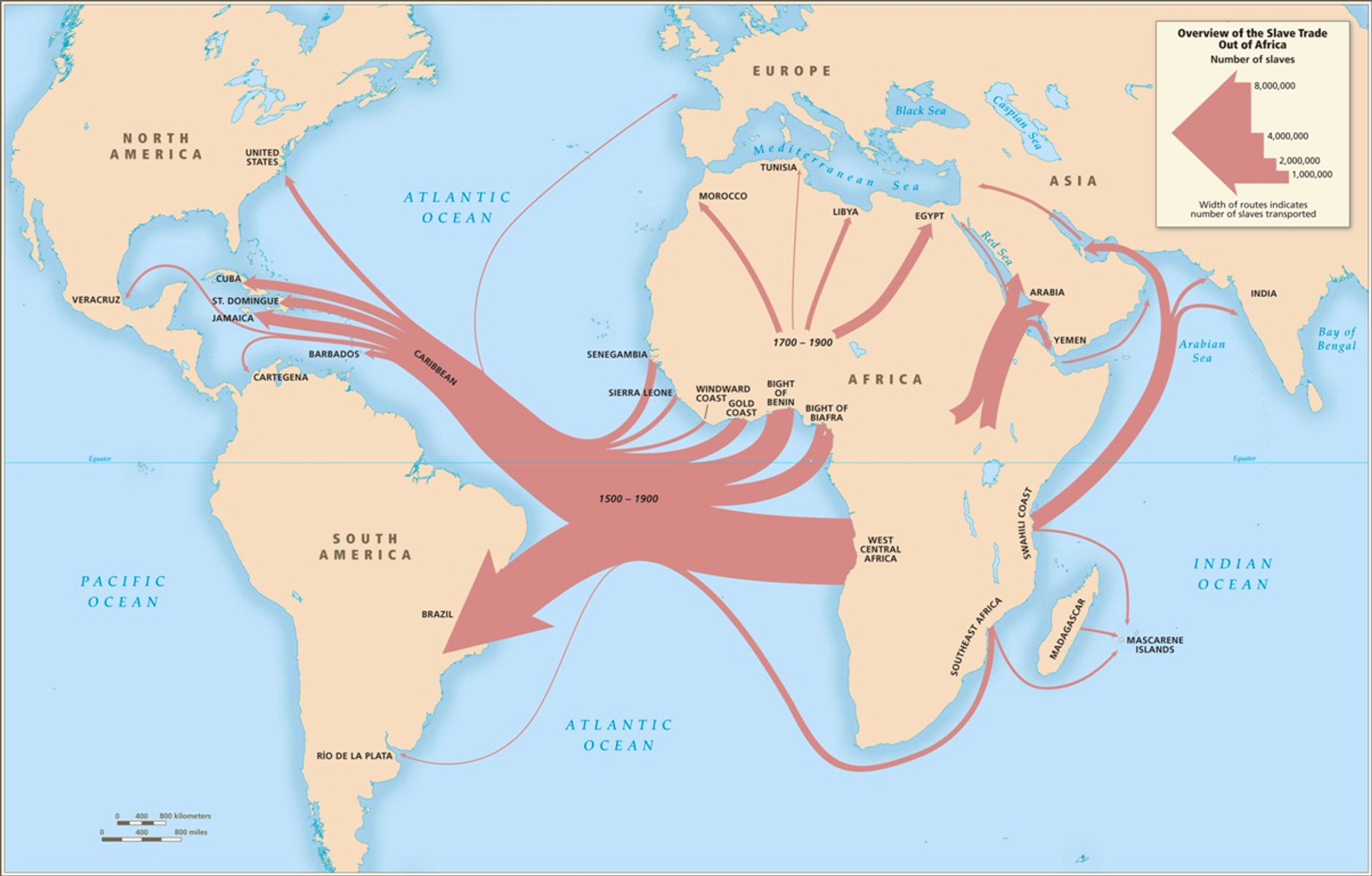
- Atlantic crossing = Middle Passage
- Slave ships were cramped and cruel, fitting slaves on the ship by stacking on top of each other.
- The process to make sugar was very dangerous, so slaves were used for sugar production.
- South American slavery had a much higher death rate, as a result.
- 12.5 Million Africans left on the Middle Passage, most to South America.
- ~2 million died; ~10 million arrived.
Becoming “American”
- We become less English, and more independent from England.
- We develop our own identity for the first time
- First Great Awakening (1730-1740)
- A Series of Christian revivals swept the colonies.
- Enlightenment/philosophy meets religion.
- Personal salvation.
- Relationships with God are normal.
- Spiritual equality → this is dangerous because there are slaves in the colonies, and spiritual equality means everyone is equal.
- This also leads to the AME church.
- They elected church leadership through voting.
Colonial Slavery 🦅
- Established in the English colonies in ~1619.
- Relatively small numbers until the 1700s.
- Most went to South America to due to the nature of the sugar plantations. (Caribbean)
- Through the middle passage.
- Slavery existed in the North and the South.
Northern vs Southern Slavery
- In the north, Slaves were more integrated into society because of cities.
- Different type of society; Worked in cities and towns.
- Northern slaves lost their cultural identity.
- In the south, slaves were more isolated (on plantations) and had larger numbers.
- used to produce cash crops.
- Maintained west African culture at a higher rate.
- Gullah and Geechee people (around Georgia).
Relationships
- Start of “paternalism”
- Slave master and Christianity could “save slaves from themselves”
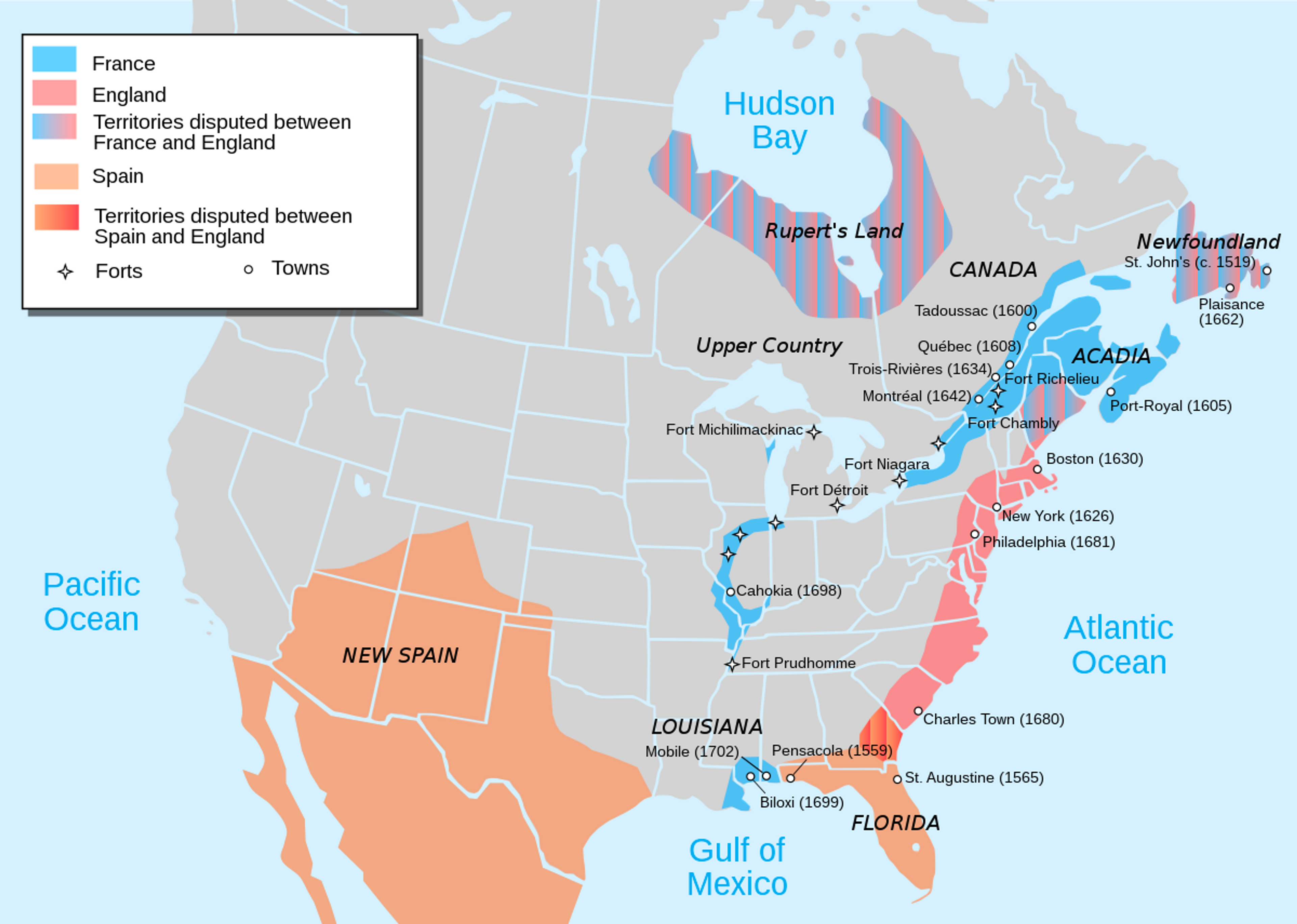
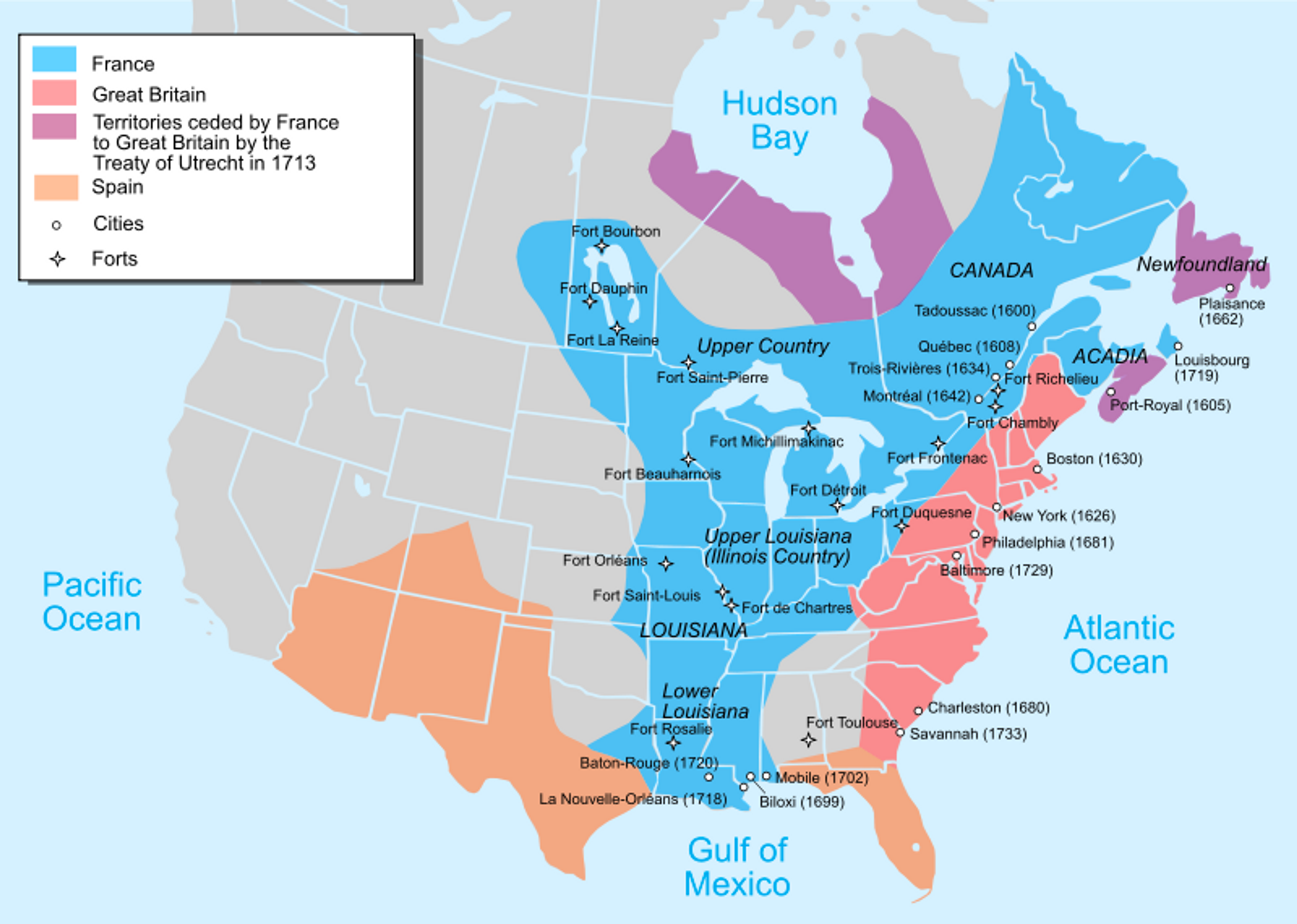
Colonial Conflict 🤺
- “Empires aren’t for sharing”
- The leaders of Europe would wage global conflicts against each other for over 100 years. (~1600 - ~1800)
- Constant European wars and shifting power would make the American colonies a theater of conflict.
- Catalyst for American Independence. ⭐️
- The conflicts in America were much smaller compared to the larger conflicts in Europe.
- Most of the conflict was between England and France.
King William’s War (1688 - 1697)
- Sideshow to the 9 years war in Europe
- Europeans and Natives raiding and backwoods fighting
Queen Anne’s War (1702–1713)
- Also known as the War of Spanish Succession
King George’s War (1744-1748)
- Also known as the War of Jenkins’ Ear
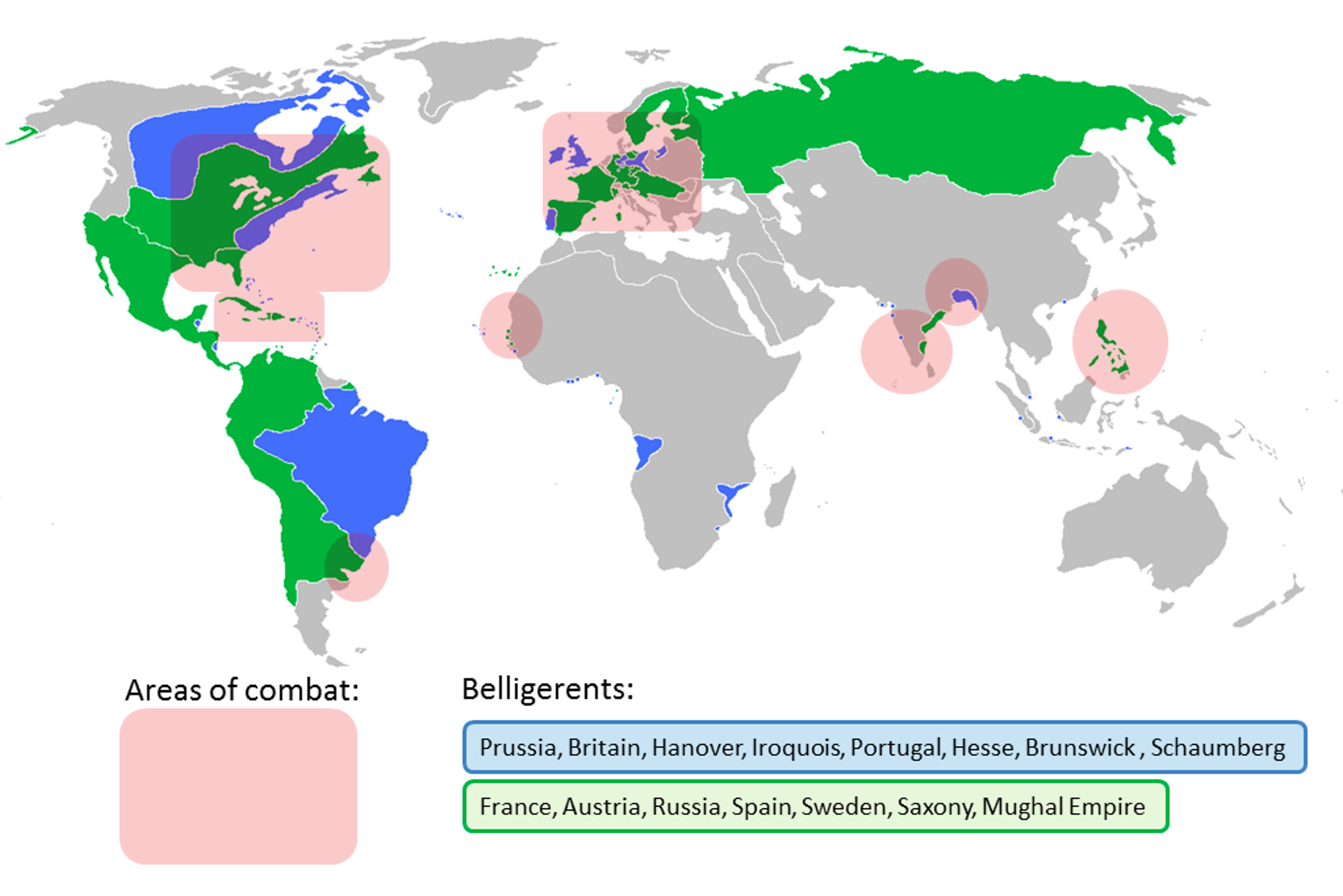
French and Indian War (1754-1763) ⭐️
- Part of the 7 years war.
- The world’s first world war. ⭐️
- During the beginning of the war, the French were winning
- Later, England outspends France and wins.
- England now has a massive war debt.
- England aims to pay the debt by taxing the colonies.
- Occupational armies were developed after the war.
- Armies would be in the colonies, sometimes living with the colonists.
- The Proclamation Line of 1763
- It stopped people from living farther west than the Appalachian mountains